rationalism international relations
It is frequently maintained that rationalism is something other than an ism of International Relations. Rationalism assumes that the most important and in fact the only entities dictating international relations are nation states and that these nation states are engaged in a zero-sum game of diplomacy and war in which the goals of every nation state is eventual dominance above all others so that international relations are dictated almost.

Presented By Yu Seunghee Zhang Luan Ppt Video Online Download
Rationalism sets a projecting framework in the International Relations assistance.
. RATIONALISM IN INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS. The major concepts usually discussed in the Rationalist International Research are as follows. 1 in at least one important respect this would.
Rationalism in Western philosophy the view that regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge. Actions are carried out sensibly underpinned by clear thinking using a reasonable mind. Fearon and Wendt 2002How to define the relationship between rationality and norms or identity has been one of the main issues in this debate.
On the narrower ground of whether rationality and rationalist models provide a basis for constructing or reconstructing the field of international relations an al- leged affinity between rational choice models and traditional state-centric views of international politics as well as a long-standing embrace of game theory has until recently. In the rational choice approach individuals are seen as motivated by the wants or goals that express their preferences as well as other incentives like reward or promise of reward Orji2009 p. Internationalism Internationalists believe in a world orderwhere an effective world governmentwould govern the world that sovereignty is an outdated concept and barrier to creating peace the need for a common humanity and the need for cooperative solutions.
This article examines major debates between rationalism and constructivism. The rationalistconstructivist debate is an ontological debate within international relations theory between rationalism and constructivism. Rationalist models have faced four persistent sets of critics as the research program of international relations has evolved.
Thus it was later criticized by reflectivists that rationalism is not the best approach to understand the international relations. Theory of international relations. The Rationalism depends on the objective processes and the preferences of many different people with their inherent values ideals prejudices etc.
Incomplete Information Credibility Trust Audience Cost. This systemic approach attempts to mirror the natural sciences in dismissing non-observable and therefore non-testable factors. Rationality in International Relations Miles Kahler The role of reason in international relations has been contested since the eighteenth century.
Rational is commonly said to be an individual that is acting logically or rationally ie. The construction of a sphere of calculated state action raison detat and an image of the balance of power suggested an Enlightenment equilibrium as compre- hensible to human reason as a clockwork. Holding that reality itself has an inherently logical structure the rationalist asserts that a class of truths exists that the intellect can grasp directly.
It presents that there are politically significant motives of. Up to 10 cash back Since the 1990s one of the major debates in International Relations IR scholarship has been between rationalism and constructivism Katzenstein et al 1998. In other words persons are to achieve their goals under certain conditions.
Rationalism in explaining international political life because solid and well-defined self-interests formed by costbenefit analysis can lead actors to forsake their normative values and identities. Rationalist theories embrace positivism to a certain extent which means they believe that the practice of IR can be reduced to simple and observable systemic rules and laws which their theories aim to document. In the introduction to the fiftieth anniversary issue of international organization peter katzenstein robert keohane and stephen krasner 1998 suggest that the main axis of debate in the field of international relations ir in the coming years is likely to be rationalism versus constructivism.
Within the realist school of international relations a prevailing view holds that the anarchic structure of the international system invariably forces the great powers to seek security at one anothers expense dooming even peaceful. CONCEPTS THEORETICAL LIMITS AND CRITICISM Douglas H. The essay is composed of three sections.
Realism theory in international relations is the most dominant school of thought after World War II and until now it has relevance in the present international politics. But to begin with I will define what is meant by rationalism in IR. Under neorealisms structural constraints of international competition and selection agents rationality may appear superfluous.
Rationalism in International Relations usually tend to explain circumstances that brings about patterns of behavior. Realism had gained its popularity from the late 1930s and early 1940s when the idealist approach had failed to analyze the real politics throughout the world. In the first section I explore the major differences between rationalism and constructivism and.
Rationalists adhere to these beliefs to some extent. Inspired by critical theory but using quantitative survey data this article takes issue with that notion arguing that rationalist work with its emphasis on interests institutions and information has a distinct logic of individualistic utilitarianism. Novelli Abstract The present paper analyzes the presence of the axiom of the rationality of the political actors in theories of International Relations and traces considerations about the concept.

Pdf Theory Synergetic Approach In Ir Case Study Of Btc And Sgc Pipelines Semantic Scholar

Realism Rationalism And Revolutionism In Iran S Foreign Policy The West The State And Islam Semantic Scholar

Rational Theory Of International Politics Princeton University Press

Pdf Constructivist Approaches In International Relations Theory Puzzles And Promises Semantic Scholar
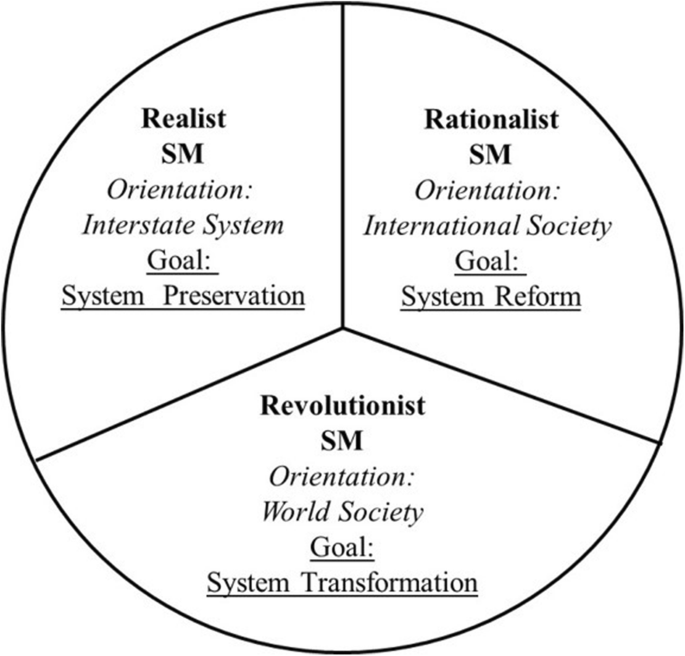
Social Movements And International Relations A Relational Framework Springerlink
How To Compare Realism And Rationalism Quora

Liberalism Radical Theories John Lee Department Of Political Science Florida State University Ppt Download

Political Science And International Relations Main Directions Of

Pdf Constructivist Approaches In International Relations Theory Puzzles And Promises

Theories Of Colonial Encounters In International Relations 41 Download Table

Realism Rationalism And Revolutionism In Iran S Foreign Policy The West The State And Islam Semantic Scholar

Amazon Com Trust In International Relations Rationalist Constructivist And Psychological Approaches Routledge Global Cooperation Series 9780367820985 Haukkala Hiski Van De Wetering Carina Vuorelma Johanna Books

Pdf From Wendt To Kuhn Reviving The Third Debate In International Relations

What Rationalist Approaches In Ir Contribute Grin

2 Fundamentals In International Relations Rationalism And Materialism Ab Foreign Service Studocu

Table 2 From How To Combine Rationalist And Constructivist Accounts Of International Politics Building Bridges On Terra Firma Semantic Scholar

Social Movements And International Relations A Relational Framework Springerlink

Table 1 From How To Combine Rationalist And Constructivist Accounts Of International Politics Building Bridges On Terra Firma Semantic Scholar

Pdf Constructivist Approaches In International Relations Theory Puzzles And Promises Semantic Scholar

Comments
Post a Comment